
Evaluating the earthquake risk of the island of Cyprus and the TRNC, the expert academics of Near East University warned that the earthquake risk we face is not at a level that will cause panic, but that the building stock should be made earthquake resistant without being complacent. According to experts, the most important step to be taken is; Creating a district-based earthquake risk map in the TRNC!
The aftershocks of the Kahramanmaraş-centered earthquakes in Turkey, some of which are also felt in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, have been continuing. The exaggerated earthquake predictions of some earthquake experts, which are reflected in the media about Cyprus, cause great uneasiness in the public. So, what is the real extent of the earthquake risk carried by Cyprus Island and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus? Near East University’s earthquake expert academics came together under the moderation of Near East University Vice Rector Prof. Dr. Mustafa Kurt and discussed the earthquake reality of Cyprus!
Near East University Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Dean Prof. Dr. Hüseyin Gökçekuş, Near East University Faculty of Engineering Lecturer Prof. Dr. Salih Saner and the Director of the Near East University Earthquake and Soil Research and Evaluation Center Prof. Dr. Cavit Atalar also created a road map for the measures to be taken and the work to be done while evaluating the earthquake risk of the island! Experts also emphasized that they will organize comprehensive scientific events at Near East University as soon as possible that will put the earthquake agenda at the center. The first of these events will be the “Earthquake Risk in the TRNC and What Should Be Done” workshop to be held on March 8 at the Near East University İrfan Günsel Congress Center. After the workshop, which will bring together academics, heads of chambers and unions and earthquake experts, between 18-22 October, the second “International Earthquake Hazard and Earthquake Risk of the Mediterranean Congress” to be chaired by Prof. Dr. Hüseyin Gökçekuş will be held.
The earthquake reality of Cyprus: There is no room for panic or complacency!
The main earthquakes affecting 11 cities in Turkey were also felt in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus. However, it is an important point that the fault line extending from Turkey to the Mediterranean does not intersect with the island of Cyprus on land. Near East University Faculty of Engineering Lecturer Prof. Dr. Salih Saner said, “There is a fault extending from Hatay to the southwest on the active fault map. Located in the east, this fault crosses 200 kilometers from Cyprus, approaching 50 kilometers from the land in the south of the island. These earthquakes, which move in the shape of a crescent in the south of the island, are unlikely to cause great destruction in Cyprus. Earthquakes that will occur on this fault line can be felt in Cyprus. If it is severe, it can also cause destruction, but I expect this fault to produce earthquakes with a maximum magnitude of 6.8 across the island and a maximum of 4 in the TRNC.
Stating that fault lines are formed at the intersection of plates that repel each other, Prof. Dr. Salih Saner said, “The African plate in our south is subducting under the Anatolian plate, on which Cyprus is also located. This movement of the African plate is decisive in earthquakes that may occur in Cyprus. However, the depth of the earthquakes caused by this situation is quite high.
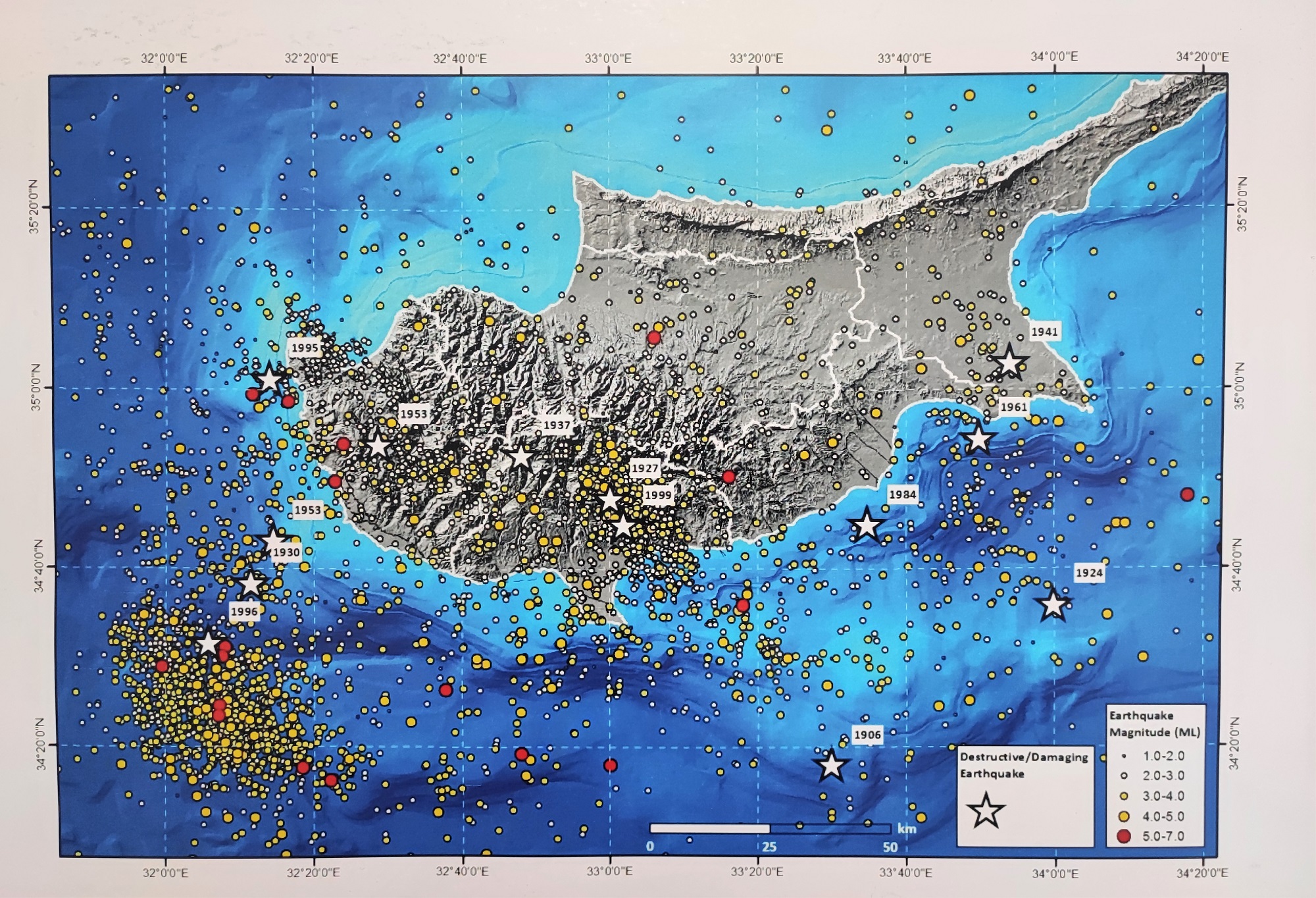
Chairman of the Near East University Earthquake and Soil Research and Evaluation Center, who is also the Chairman of the TRNC Presidency Earthquake Committee, Prof. Dr. Cavit Atalar, on the other hand, said that in the last 130-year history of Cyprus, there have been 15 devastating earthquakes, the biggest of which were in 1941, 1953, 1995, 1996 and 1999. Prof. Dr. Atalar informed that while the successive earthquakes of 6.0 and 6.1 that occurred in Paphos in 1953 had an impact of 8 in the region, this effect was felt at the level of 5 in Nicosia. “The largest earthquake ever recorded in Cyprus occurred in 1996 and was 6.8 magnitude. When we look at the current situation, an earthquake can happen in Cyprus at any time. However, it is not possible to predict where, when and how large an earthquake will occur. The important thing is that the buildings are built on solid ground.
The point that experts agree on is that the earthquake risk in Cyprus is not at a level to cause panic. However, the experts, who emphasize that the main issue that determines the destruction and loss of life in earthquakes is building safety, point out the necessity of providing earthquake-resistant construction without being complacent.
Earthquake risk is higher in the South!
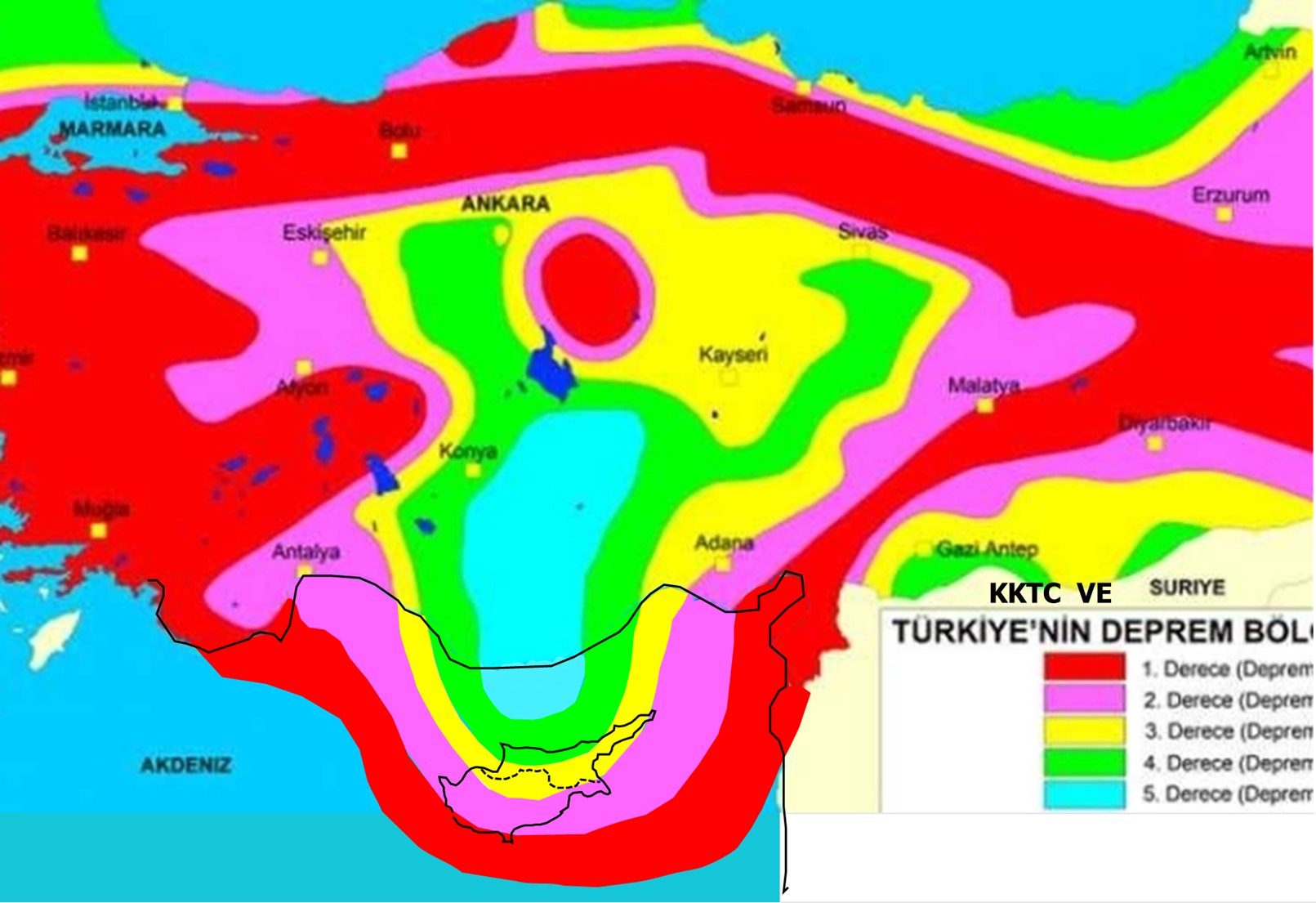
Reminding that the biggest earthquakes affecting Cyprus occurred in Limassol and Paphos when we look at the historical data, Near East University Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering Dean Prof. Dr. Hüseyin Gökçekuş said, “The earthquake-producing region, which we call the Cyprus arc, is located in the south of the island. Therefore, the earthquake risk is much higher in the South. The main factors that determine the destructiveness of an earthquake are the size of the broken fault, the duration and depth of the earthquake. However, another issue that is as important as these is the durability of the buildings. Therefore, what needs to be done is to determine the earthquake risk of the building stock throughout the TRNC as soon as possible. Prof. Dr. Salih Saner’s words “I expect the current faults to produce earthquakes with a maximum magnitude of 6.8 in the whole island and a maximum of 4 in the TRNC” confirms Gökçekuş’s findings.
In the “Earthquake Risk Map” created by Prof. Dr.Salih Saner by combining the fault and earthquake maps of Turkey AFAD and MTA and historical earthquake data of Cyprus, it is stated that Paphos and its surroundings are the most important earthquake region and the earthquake risk is more intense in Southern Cyprus. Prof. Dr. Cavit Atalar, on the other hand, expresses his objection to this map by arguing that “When we consider today’s earthquakes and historical earthquakes, the East Anatolian fault zone goes south from the land to Syria, Lebanon and Israel after Hatay.”
District-based earthquake risk map should be created in TRNC!
The earthquake experts of the Near East University also agree that district-based earthquake risk maps should be created in order to determine the earthquake risk of the island of Cyprus and the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus. Stating that micro zoning work should be done as soon as possible in the TRNC, Prof. Dr. Cavit Atalar says that after the regional earthquake risk maps are created, the earthquake risk of the country will be evaluated much more realistically.
Prof. Dr. Hüseyin Gökçekuş, emphasizing the importance of regional earthquake risk maps, said, “This study should be carried out in cooperation with universities and the public, with international support. In this study, in which many experts from different fields should come together, the earthquake resistance of the building stock, the characteristics of the soil of the regions, the determination of active and dormant fault lines, and seismicity analysis should be completed comprehensively and the risky areas should be determined.
Building stock must be analyzed
One of the most important issues emphasized by the experts is the need for earthquake analysis of the existing building stock. Reminding that they modernized the equipment of the Building Materials and Soil Mechanics Laboratory within their faculties, they opened them to the public for earthquake analysis of the structures. Dr. Hüseyin Gökçekuş, “We started the first studies on the Near East University campus. We measure the durability of the samples we take from the structures with the core drilling machine, by putting them through pressure tests in a laboratory environment. With the reinforcement scanning test, we quickly determine the diameter and density of the reinforcement bars used in structural elements such as columns and beams of buildings, without any breaking. After making the ground analysis, we analyze all the data with the relevant computer software and determine the reinforcement requirements of the buildings.” Prof. Dr. Gökçekuş, accepting the date when the earthquake regulation came into force in the TRNC as a milestone, emphasized that these tests should also be carried out for the building stock in the TRNC, starting with the structures built before.